Future of SaaS: Key trends and architecture insights

Why users expect more from SaaS product architecture
SaaS has evolved far beyond its early days of browser-based tools and one-size-fits-all platforms. In 2025, it stands as the dominant software model, powering organizations of every size. The future of SaaS is shaped by smart product architecture, deeper user engagement, and continuous value delivery across every touchpoint. People now expect platforms to be adaptive, scalable, and personalized. Users demand AI-powered tools, seamless integration, and feature sets that align with real workflows.
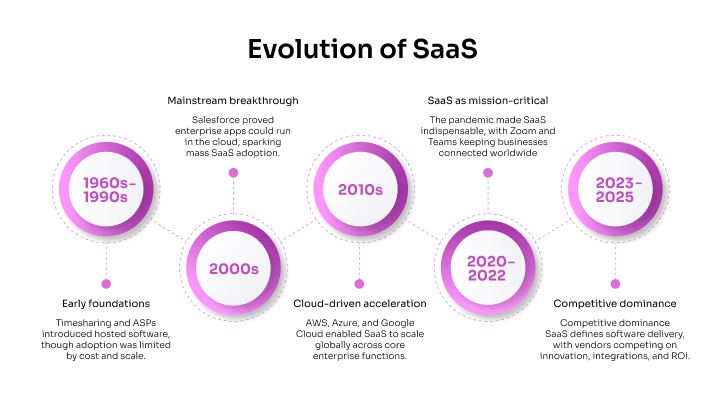
Evolution of SaaS adoption: From the 1960s to today
SaaS has changed over time because more people want it, connections have gotten better, and infrastructure has gotten better. Some of the most important things that happened are:
The earliest concepts resembling SaaS emerged in the 1960s. These were timesharing systems that enabled many people to use the same computer from different places. Application Service Providers (ASPs) offered hosted software online in the 1990s, but they had challenges with high fees, limited bandwidth, and scaling.
Salesforce released a CRM that worked on a web browser in 1999. This indicated that corporate software could work entirely in the cloud. In the 2000s, the invention was a giant stride forward. SaaS became increasingly popular since it was cheaper and easier to use than older models that needed servers on-site.
Speeding up with the cloud (2010s): AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud all grew popular. These cloud services gave SaaS companies the tools they needed to expand their enterprises worldwide. Companies place items like HR, finance, CRM, and working together in the clouds that are vital. SaaS became a scalable alternative to local systems, which made it easier to come up with new ideas and add new features all the time.
SaaS as a mission-critical service (2020–2022) People all across the world started using SaaS because of the COVID-19 pandemic. People utilized Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Slack more because they worked from home or in a hybrid setting. Businesses required SaaS to keep running even when there were disruptions like lockdowns.
By 2025, SaaS will be the most common way to receive software. Every day, businesses use it to communicate with customers, perform analytics, and get in touch with them. There is a lot of competition in every field. It's easier for small and medium-sized firms to move, but it's tougher and pricier for huge businesses that use Microsoft 365, Salesforce, or SAP to do the same. Vendors compete with each other by coming up with new ideas, using current stacks, and showing that they can make money.
SaaS market outlook: Segmentation and future opportunities
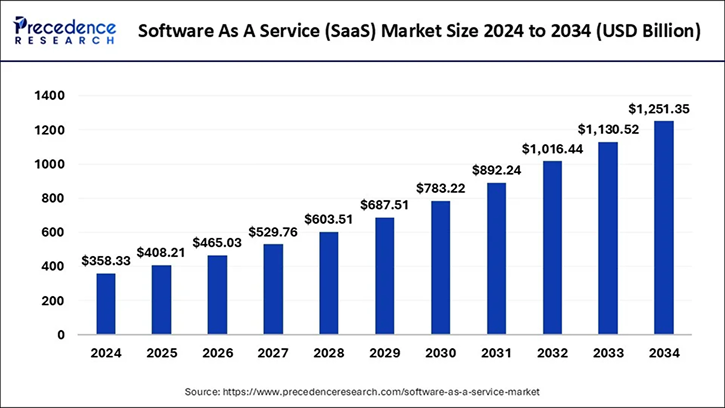
Market size
The SaaS market is expected to maintain strong momentum throughout the next decade. According to Precedence Research,the global market size will grow from USD 358 billion in 2024 to USD 1,251 billion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of nearly 20% (Precedence Research). This steady rise underscores the growing reliance of organizations on cloud-delivered services and the critical role of SaaS in digital transformation strategies.s.
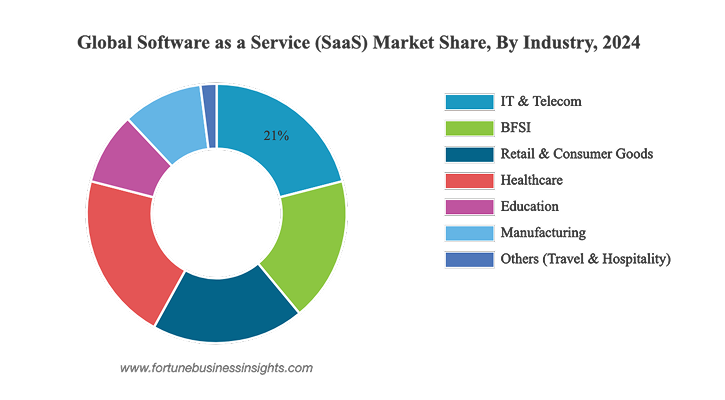
Distribution by industry
Education, manufacturing, and travel and hospitality also make steady contributions, indicating how SaaS is useful in both digital-first and conventional businesses.
This industry distribution indicates that SaaS has grown beyond technology-focused industries and become a standard way to deliver services in many different fields.
SaaS adoption spans nearly every sector, but a few industries are driving the largest share of revenue. In 2024, IT & telecom dominated the market, holding the leading share due to strong demand for secure, AI-driven applications. A PwC survey found that 84% of IT executives view SaaS solutions as more secure than on-premises alternatives, while about 57% of telecom companies already use AI-powered SaaS to improve customer service and operational efficiency (Fortune Business Insights).
The healthcare sector sustains 22% of the market share in 2025 and is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 26% over the forecast period. Healthcare providers are migrating applications and storage to the cloud to support hybrid work and telemedicine. SaaS platforms provide real-time access to patient data, simplify storage management, and reduce IT system complexity. Telemedicine technologies such as video consultations, telesurgery, and teleradiology are driving adoption further.
Other important verticals include BFSI, retail & consumer goods, education, manufacturing, and travel & hospitality. Together, these segments show that SaaS has expanded beyond technology-heavy markets and established itself as a standard delivery model across diverse industries.
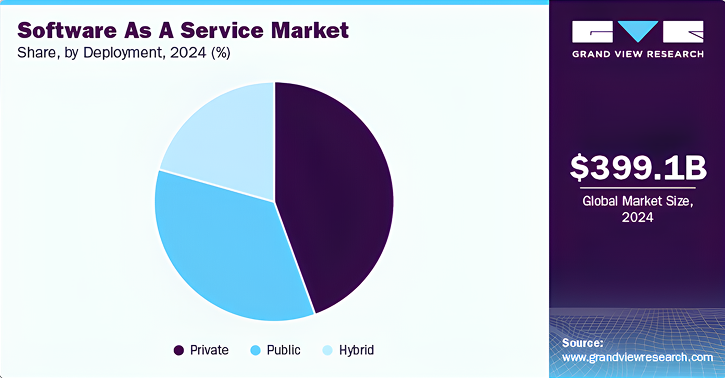
Thoughts on deployment
Deployment strategies mean that people still use SaaS in different ways. According to Grand View Research, the private cloud sector made the most money in 2024 (Grand View Research).
Businesses have more control over their data and infrastructure when they use private clouds, and these clouds also help them follow the rules. When used with edge computing, they also lower latency, which makes apps that need speed and reliability run better. This combination gives many businesses the right amount of control, safety, and speed to get SaaS apps to a lot of people.
Hybrid and public deployments are still important, especially for businesses that want to be able to change things up and save money. But for businesses that need strict data control, private cloud is the best option.
How innovation drives SaaS competitiveness
High competition and low tolerance for stagnation define the SaaS market in 2025. Thousands of platforms serve overlapping functions, and switching costs for many customers are manageable. In this environment, the pace of innovation often determines which vendors gain market share and which lose relevance.
Innovation changes the way businesses compete in several ways:
Product velocity. Vendors that deliver frequent updates and improvements demonstrate responsiveness to user needs and market changes. Regular feature releases have become an essential requirement for building user trust and ensuring retention.
Ecosystems for integration. Modern SaaS products compete as standalone solutions and as parts of larger digital ecosystems. Platforms that expand through APIs, partnerships, and marketplaces position themselves more strongly than isolated products.
Adoption of emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation are becoming standard elements in SaaS. Companies that successfully embed these capabilities improve efficiency, decision-making, and personalization — strengthening their competitive advantage.
User-centric innovation. Innovation that reduces friction, simplifies workflows, and enhances accessibility directly translates into higher adoption and lower churn.
Competitiveness in SaaS is shaped by pricing, functionality, and the ability to innovate. Vendors that sustain a culture of continuous improvement, combining technical advancement with customer feedback, set the pace for the market. Companies that fail to adapt and evolve quickly risk being displaced by more agile competitors.
This competitive environment also shows how user expectations are changing. Digitally mature customers compare every platform with the best experiences available, which makes product success increasingly dependent on understanding user behavior. The following sections explore these behaviors in detail and highlight the product features that define a modern SaaS platform.
10 user behavior trends shaping SaaS
SaaS expectations have accelerated, driven by digital maturity, rising competition, and the influence of consumer-grade products. Buyers now assess platforms on how effectively they integrate into workflows, safeguard data, and adapt to evolving needs.
The ten trends below highlight the key developments in user behavior in 2025–2026. They cover personalization, AI-native design, flexible pricing, sustainability, and other priorities that define how SaaS products are evaluated today.
Trend 1: Personalization and adaptive UX
According to Twilio Segment, 89% of marketing leaders consider personalization essential for future success, and research shows that customers are willing to spend up to 38% more with brands that deliver it effectively. These findings show that personalization plays a central role in user satisfaction and revenue growth.
Personalization that works includes dashboards based on roles that provide relevant metrics, onboarding that changes based on what the user has done before, and contextual nudges that suggest what to do next. For example, email platforms might show campaign analytics that are relevant to marketers or sales leaders, support tools might show answer templates based on past situations, and productivity apps might suggest ways to connect with calendars or CRMs.
Trend 2: Data protection, transparency, and trust
High-profile breaches and stricter enforcement of regulations such as GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in U.S. healthcare, and CCPA in California have made organizations more careful about where data resides.
Consumers now demand clear details about the data collected, its usage, and the available controls. People trust platforms more when they provide privacy dashboards, explain permissions in simple terms, and let people opt out.
This demand for transparency alters the way products are developed. Collaboration tools show certifications like SOC 2 or ISO 27001, HR systems have modules for managing consent, and productivity apps send alerts in real time for strange behavior. These features make security and openness a part of the daily user experience.
Trend 3: AI-powered assistance and workflow automation
Users expect AI to guide, predict, and automate tasks inside the tools they use every day, and adoption confirms the trend: McKinsey reports that 78% of organizations now rely on at least one AI capability in their operations.
AI is built into modern SaaS in ways that don't feel like they're there. Project management software make draft timelines based on the history of tasks, customer care platforms suggest how to respond to new tickets, and sales systems automatically score leads to show the greatest chances. These functionalities are built into workflows, so AI is a normal part of how work gets done.
The infographic below shows the most important ways that AI will change SaaS in 2025 and beyond. Some important topics are predictive analytics, tailored suggestions, automated workflows, and finding fraud.

Trend 4: Mobile-first and cross-platform consistency
People expect mobile apps to work the same way as desktop apps, with synced states and workflows that don't stop between laptops, tablets, and phones. This expectation has grown along with hybrid work, where people switch between devices all the time.
Real-world examples show how things have changed. Design tools automatically save projects so that work started on a desktop can continue on a tablet. To avoid gaps, collaboration apps keep a history of notifications across devices. Analytics platforms keep dashboards in sync in real time, so users can make reports on a computer and show them on a phone without any problems.
In fields like sales, logistics, and field services, where mobile access is essential to daily operations, reliable cross-platform performance is now a must. Users tend to favor platforms that function seamlessly across all their devices, swiftly replacing those that don't.
Trend 5: Embedded support and self-service as part of product UX
Slow responses or complex ticketing quickly drive users to alternatives, most often in competitive markets. Support is now viewed as part of the product experience rather than a separate channel.
Modern platforms embed help directly into the interface. Resource centers provide FAQs, tutorials, and walkthroughs without disrupting workflows. AI assistants handle routine questions or direct users to relevant content, while live chat and contextual ticketing resolve more complex issues.
The graphic below outlines common chatbot types now used in SaaS support. The most effective models combine speed with autonomy. Users troubleshoot independently when possible while maintaining easy access to human support.
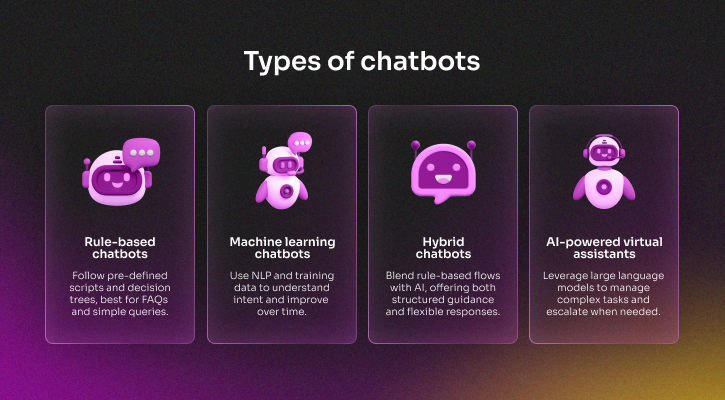
Trend 6: Accessibility and inclusive design
Organizations now check to see if platforms meet global standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) and work with assistive technologies like screen readers, keyboard navigation, and voice commands. Accessible design goes beyond following the rules; it directly affects how many people use and keep using a product by making sure it works for everyone on a team.
More and more collaboration tools are adding high-contrast themes and captions for video calls. Productivity platforms make interfaces easier to read by using scalable fonts and a clear visual hierarchy. HR and learning management systems support multiple input methods to accommodate different abilities.
Inclusive design communicates product maturity, expands accessibility for diverse teams, and reduces the risk of churn caused by usability barriers.
Trend 7: Low-code / no-code control and customization
Low-code and no-code (LC/NC) features are now a key part of modern SaaS. They let business users make workflows, dashboards, and simple apps without needing developers, which makes businesses more flexible and speeds up deployment cycles.
Today, marketing platforms come with visual builders for automated campaigns, analytics tools have drag-and-drop dashboards for people who aren't tech-savvy, and HR systems have templates for surveys or approval flows. These features make it easier for people in roles that used to avoid technical configuration to use the software.
The hard part is finding the right balance: customization needs to be easy, stable, and safe. Providers that do this get customers to adopt their products faster, keep them longer, and make more money over time.
Trend 8: Integration and interoperability as must-haves
Organizations now depend on multi-app workflows, making seamless data exchange across tools essential. Open APIs, prebuilt connectors, and real-time synchronization are core requirements that drive adoption and long-term usage.
Examples show the impact clearly: sales teams want CRMs that link with marketing automation and support platforms; finance departments expect accounting software to integrate with payment systems and ERPs; collaboration tools deliver the most value when tied into calendars, chat apps, and project management software.
Strong interoperability anchors a platform within the broader stack, turning it into an indispensable part of daily operations.
Trend 9: Sustainability and ethical tech signals
Increasingly, buyers want to see proof that a company uses energy efficiently, reports its carbon emissions, and follows ethical AI standards. Vendors that are open about these things make their evaluations more credible.
Cloud providers already have dashboards that show how much energy is being used and where it comes from. Some SaaS platforms focus on data center partnerships that promise to be net-zero, while others that handle sensitive data focus on AI models that can be explained and limits on monetization to follow rules and meet public expectations.
Even though small and medium-sized businesses don't care as much about sustainability when they buy things directly, it still affects how people see and trust brands. Platforms that are clear about their environmental and ethical practices are seen as forward-thinking, which increases loyalty and competitiveness in business markets.
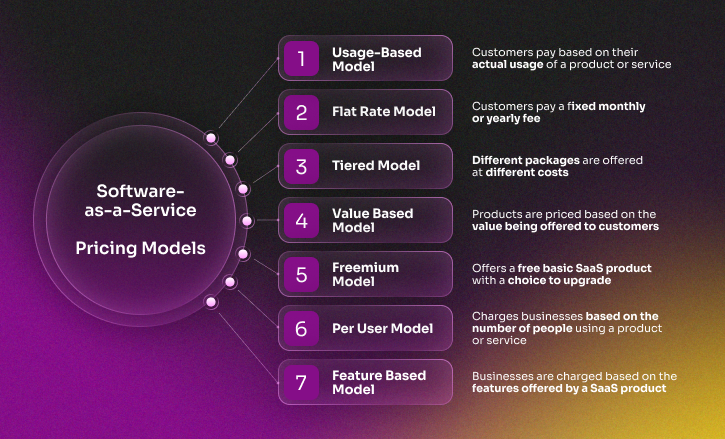
Trend 10: Flexible, usage-based, and value-aligned pricing
As subscription fatigue grows, strict flat-rate plans often don't meet the needs of all buyers. Companies are now interested in modular subscriptions or usage-based models, which charge more as usage and results go up.
This trend can be seen in all groups. Infrastructure companies are making pay-as-you-go billing more common. Productivity suites are adding modular upgrades for analytics or security. Engagement tools charge by active users to match costs with adoption rates.
To avoid confusion, success requires accurate tracking, open billing, and clear communication. Providers that are flexible and easy to work with build loyalty, while those that are stuck in rigid structures risk falling behind competitors that are more adaptable.
These ten trends make one point clear: SaaS success increasingly depends on aligning with user behavior. Products that personalize experiences, embed AI responsibly, ensure seamless interoperability, and offer transparent pricing earn loyalty in a crowded market.
Key features SaaS users expect
People will or won't use SaaS depending on whether or not the platforms have the basic technical features that consumers expect these days. AI help, analytics, strong security, an easy-to-use design, and seamless integrations are all features that a product should have, not things that make it stand out. To make sure that products stay reliable, compliant, and adaptable, each capability must be backed up by good engineering practices, scalable architecture, and clear execution.
AI-powered features and workflow automation
People use SaaS products to automate tasks they do over and over, get information right away, and switch to new tasks as they come up. Support platforms write responses to tickets, project management tools guess how risky a delivery is, and CRMs rank leads based on how likely they are to become customers. These features make workflows easier and add value to the product as a whole.
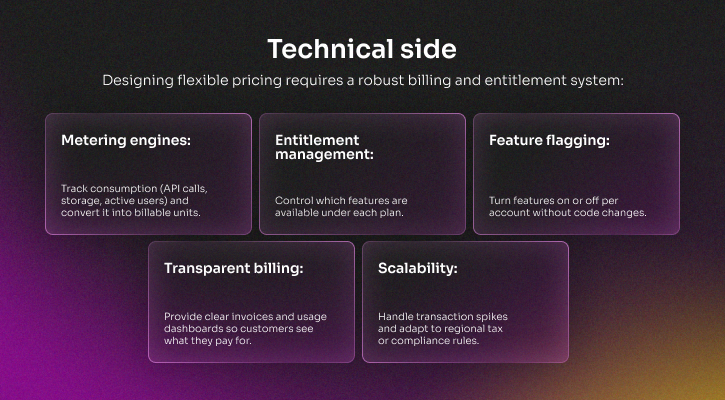
Strong implementation needs inference pipelines that work in real time, cloud resources that can grow, and constant monitoring. These things work together to make sure that AI stays accurate and responsive even when more people use it. This means that SaaS apps can always count on automation.

Explore how we integrate AI in product
Advanced analytics and decision dashboards
Dashboards in SaaS are now places where you can make decisions in real time. Marketing teams keep an eye on how well their campaigns are doing in real time, finance teams make live predictions, and operations managers get automated alerts when metrics go outside of expected ranges. Predictive insights and anomaly detection are now standard, which helps teams move faster and with more confidence.
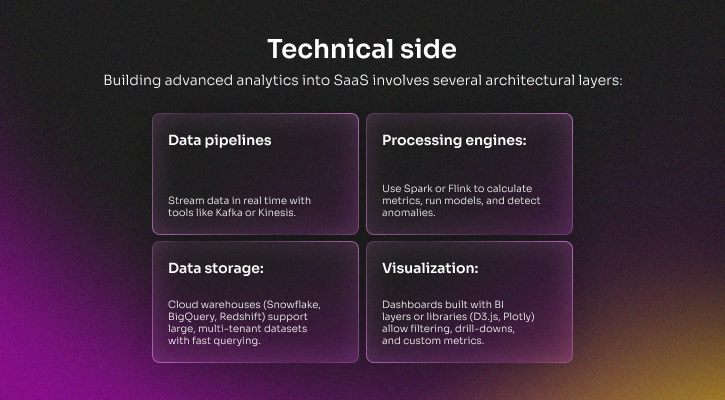
Key technical problems include keeping tenant data separate, using role-based access control (RBAC) for sensitive access, and reducing latency so that results can still be acted on.
Data privacy, compliance, and user control
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government require SaaS platforms to meet strict compliance standards before adoption. Beyond meeting regulations, users expect clear visibility into how their data is collected, stored, and shared, with tools that give them meaningful control.

Implementation often includes privacy dashboards, consent management APIs, and deployment options aligned with regional data residency rules. These features reduce legal risk, speed up procurement, and build long-term trust.
API-first design and seamless integrations
People expect modern SaaS products to work well with other software, like CRMs, ERPs, analytics, and messaging systems. API-first architecture makes sure that integrations are stable and can grow, instead of being added on later.
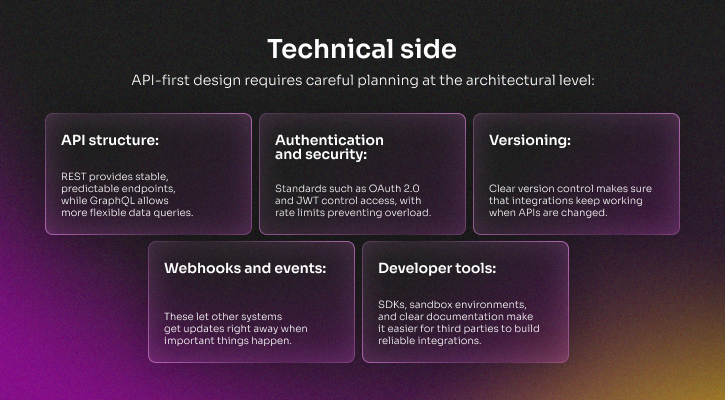
Platforms that extend this with marketplaces or prebuilt connectors (Zapier, Workato) provide faster interoperability, helping the product embed deeply into workflows and increasing long-term adoption.
Modular subscriptions and usage-based pricing
People are getting tired of subscriptions, which has changed their expectations for prices that match real use and value. Companies don't want fixed tiers; they want modular plans for certain features or usage-based billing that is based on consumption, adoption, or outcomes. This flexibility builds trust and makes it easier to explain why you should renew.
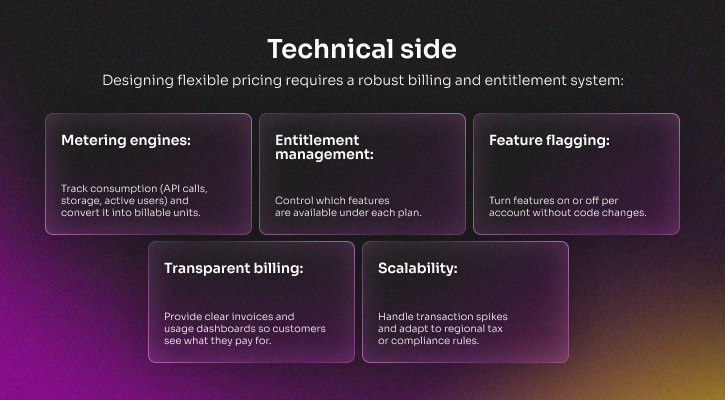
A strong pricing system also lets for hybrid models, like a base subscription plus usage-based overage, which keeps customers happy while also helping vendors make more money.
Accessible and inclusive product design
Accessibility has become a purchasing requirement in regulated industries and an indicator of product maturity across all markets. Inclusive SaaS design ensures usability for people with disabilities, varied language needs, and different levels of digital literacy. It reduces churn, widens the customer base, and signals product quality.
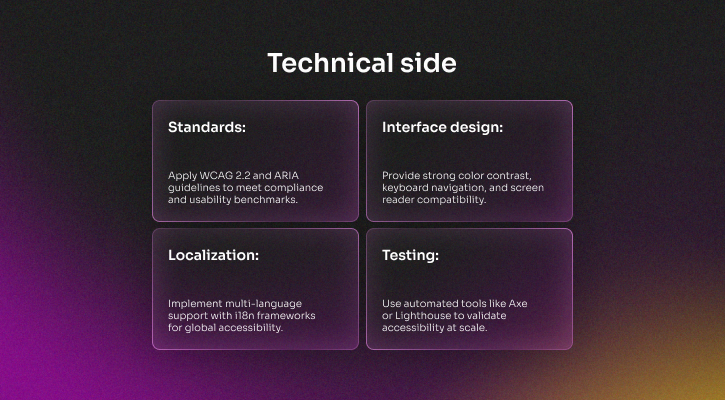
Accessible and inclusive design reduces compliance risk while strengthening competitiveness in enterprise procurement.
Offline access and low-latency performance
In sectors like logistics, field services, or regions with unstable internet, SaaS tools must stay usable with limited or no connectivity. Users expect data to remain accessible offline and sync reliably once connections are restored, alongside real-time responsiveness in critical workflows.

This approach ensures continuity for users in the field and maintains performance standards in bandwidth-sensitive environments.
Real-time collaboration and live sync
Collaboration is now a built-in expectation in SaaS products. Users want to co-edit documents, view live updates, and exchange feedback without switching to external tools. Embedding these capabilities keeps workflows centralized and increases platform stickiness.
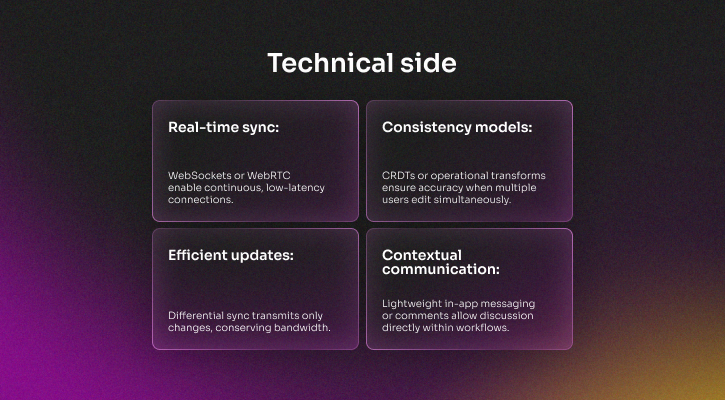
When implemented correctly, these features transform SaaS platforms into collaborative environments rather than standalone applications.
Integrated support and self-service tools
Users expect to resolve issues instantly inside the product through AI assistants, searchable knowledge bases, or live chat for complex cases. Speed and autonomy are central to satisfaction, particularly in competitive markets where switching costs are low.
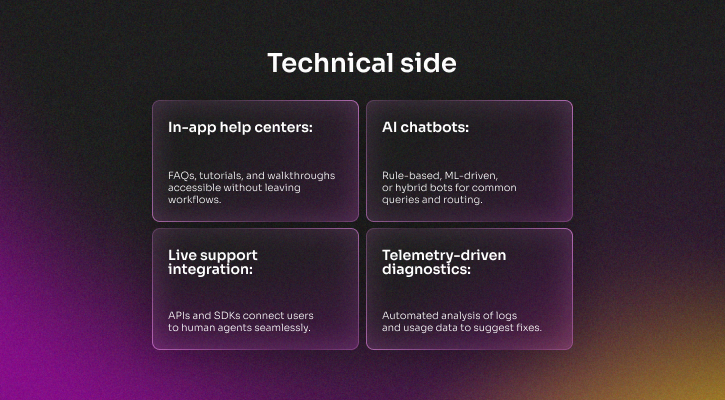
This layered model solves most issues immediately while reserving human support for exceptions, lowering vendor costs, and increasing user confidence.
Continuous updates and visible product evolution
Frequent updates show that a product is actively maintained, while changelogs and in-app notifications reassure customers that progress is ongoing and feedback is shaping development. Platforms that fail to demonstrate this risk are seen as stagnant.
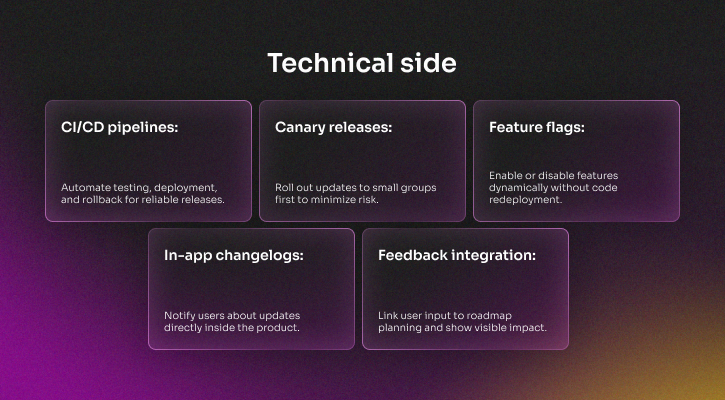
This approach keeps products secure and modern, while reinforcing trust by making evolution transparent and user-driven.

Want to customize your website?
Together, these features define what users consider enterprise-ready SaaS. Vendors that invest in strong technical foundations, such as secure data handling, real-time collaboration, and continuous delivery, position their products as dependable and future-proof. Vendors that ignore these expectations risk being outpaced by competitors who treat technical excellence as part of the user experience.
Leetio’s perspective: Building SaaS products that meet future expectations
Our goal at Leetio is to help product teams make SaaS platforms that meet the needs of today and get ready for those of tomorrow. We turn changing user behavior, technical needs, and market pressures into a clear path to making products that are strong and ready for the future. Here is a six-step playbook that shows how we do this work in a practical and defensible way that fits with what we know will happen in 2025.
Step 1: Model the full user journey across the product lifecycle
The first step in making SaaS is to figure out how people use the system in different situations. We map out the entire process, from onboarding to daily tasks to billing, cancellations, and support. We also set measurable limits like performance budgets, latency targets, and error-handling requirements.
This approach ensures no last-minute surprises by integrating authentication with analytics, billing with compliance dashboards, and support with notification pipelines. By treating the journey like a technical map, we make it clear what each part needs to do to be successful and what it needs to depend on.
 Step 2: Build scalable SaaS architecture with isolation and observability
Step 2: Build scalable SaaS architecture with isolation and observability
We must address scale and compliance at the earliest stage of product design. We place architectural principles at the core of the system to avoid costly rework later.
We implement multi-tenant or hybrid tenancy that includes strong isolation and clear migration paths.
RBAC, audit logs, and data residency rules are integrated directly into the architecture.
Event-driven layers, modular services, and feature flags so components can evolve independently.
Observability that covers traces, logs, metrics, and, when relevant, model-level monitoring, such as drift and inference latency.
 Step 3: Design modular, transparent, and adaptable SaaS products
Step 3: Design modular, transparent, and adaptable SaaS products
Adaptability in product design reduces risks during growth, and transparency in pricing builds confidence in long-term use. Our approach focuses on:
Feature flags, dynamic rollout, and canary releases to introduce new functions in controlled stages.
Modular subscriptions and usage-based billing that let companies align cost with adoption, including variable features such as AI-driven modules.
Usage dashboards that provide customers a clear view of consumption and spending.
Open APIs and integrability so the platform connects seamlessly with existing workflows.
 Step 4: Show product evolution through continuous delivery
Step 4: Show product evolution through continuous delivery
SaaS platforms remain relevant when their development is visible to customers. We set up processes that make updates clear and reliable:
CI/CD pipelines with observability alerts and rollback options to support frequent releases.
In-app changelogs, release notes, and tooltips to highlight new features and improvements.
Feedback loops that connect product metrics and user actions to future development priorities.
 Step 5: Implement security by design at every layer
Step 5: Implement security by design at every layer
Security is a foundation for trust and adoption in every market, particularly in regulated industries. We integrate protective measures into architecture rather than addressing them as afterthoughts:
We implement data encryption both in transit and at rest, along with secure key management.
Zero-trust access models and multi-factor authentication.
Continuous vulnerability scanning and automated patching.
GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations align with privacy dashboards and consent management.
This method reduces risk, accelerates procurement, and positions the product as a safe choice for enterprise deployment.
 Step 6: Scale globally with sustainability and compliance in mind
Step 6: Scale globally with sustainability and compliance in mind
The efficiency of modern SaaS products, which operate across regions, is just as important as their features. Our approach includes:
Localization of interfaces, currencies, time zones, and compliance rules.
We offer deployment options that align with regional regulations regarding data residency.
Cost-aware cloud architectures that optimize compute and storage.
Attention to sustainability through energy-efficient infrastructure and transparent reporting.
 Each of these steps reflects how Leetio approaches SaaS development as a full journey rather than a collection of isolated tasks. By combining user-centered design, scalable architecture, transparent business models, continuous delivery, embedded security, and global readiness, we give product teams the structure to compete in 2025 and beyond.
Each of these steps reflects how Leetio approaches SaaS development as a full journey rather than a collection of isolated tasks. By combining user-centered design, scalable architecture, transparent business models, continuous delivery, embedded security, and global readiness, we give product teams the structure to compete in 2025 and beyond.
For us, the real value lies in execution: sitting with client teams, embedding compliance into design, stress-testing for scale, and keeping evolution visible. This hands-on approach turns strategy into working platforms that win trust, pass enterprise audits, and adapt to new markets without losing momentum.
Final Thoughts
Software as a Service (SaaS) has advanced well beyond browser-based software delivery. By 2025, it serves as the operational foundation for a wide range of sectors, including media, logistics, healthcare, and fintech. User-centered design, robust architecture, responsible AI, transparent business models, continuous delivery, strong security, and sustainable scaling must all be balanced when creating platforms that are ready for the future.
At Leetio, we take a methodical approach to this problem. We assist product teams in developing SaaS solutions that are reliable, flexible, and relevant over time by fusing technical accuracy with an eye toward the future.
FAQ
- Growth is fueled by three main forces: the global move to subscription and usage-based pricing, the integration of AI into everyday business workflows, and the rising demand for secure, compliant platforms across regions. SaaS has become the primary delivery model for enterprise and consumer software, supported by cloud maturity and market expectations.
- SaaS will move toward industry-specific platforms, output-based pricing, and AI-enabled workflows that extend beyond automation into decision support. Sustainability metrics will influence procurement, with energy-efficient cloud operations part of vendor selection. Greater interoperability will also be expected, as organizations demand seamless data flow across digital ecosystems.
- A common mistake is underestimating regional data regulations or delaying localization of interfaces, currencies, and support. Relying on a single cloud region creates performance bottlenecks and compliance risks. Some companies also overlook sustainability metrics that are now part of enterprise procurement. Running scale simulations — testing workloads, billing flows, and latency in multiple regions — reduces surprises and accelerates adoption.
- Features that automate manual work, provide actionable analytics, and connect seamlessly with existing systems deliver the highest ROI. Examples include workflow automation, real-time dashboards, flexible billing modules, and embedded AI services that improve the accuracy and speed of decisions.
- AI is now applied to anomaly detection, predictive analytics, document processing, personalization, and automated reporting. These capabilities shorten workflows, improve accuracy, and enable new pricing models such as output- or token-based billing.
- Leetio works with product teams through a structured playbook: mapping user journeys, building scalable architectures, embedding AI responsibly, designing transparent business models, implementing continuous delivery, strengthening security, and planning for global scaling. This approach ensures that modernization is technically sound and aligned with future expectations.
CONTACT US

Sergii Kulikovskyi
Chief Executive Officer at Leetio
For detailed questions about products, their launch, or scaling.

Tanya Ivanishyna
Business Development Manager at Leetio
For questions about how our team can support you.
OUR OFFICE
Kaupmehe 7-120
10114 Tallinn
Estonia
C/ d'Aragó 562
Barcelona
Spain